React Scheduler 简析
概述
Scheduler 是 React 内部使用的调度包,但并不依赖 React,用于具有优先级的任务调度。在浏览器环境中,它能够做到:
- 以优先级动态调度任务;
- 将任务按时间片,划分到不同的宏任务(Macro Task)中,使得能够阶段性将控制权归还给浏览器;
在此基础上,SchedulerWithReactIntegration.old(new).js 文件桥接了 React 与 Scheduler 包,使得 React 内部能够间接使用该库。
本文将以源码的角度分析 Scheduler 包的实现。
任务(Task)
Scheduler 提供了 unstable_scheduleCallback(priorityLevel, callback, options) API 用于以优先级 priority 调度一个 callback,该 callback 会被封装为一个任务。任务的数据结构为:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8interface Task { id: number; // 任务 ID,从 1 开始自增 callback: Function; // 任务 callback,一个任务的核心即执行该 callback priorityLevel: PriorityLevel; // 任务的优先级 startTime: number; // 任务的开始时间,该值会影响任务的执行时机 expirationTime: number; // 任务的过期时间,该值由 priorityLevel 与 startTime 计算得到 sortIndex: number; // 任务排序标准,在容器中使用 }
对于这一数据结构,我们需要关注以下问题:
- 任务有哪些优先级(
priorityLevel)? - 任务的开始时间(
startTime)与过期时间(expirationTime)有何意义?如何计算得到? - 任务维护在哪种容器中?
优先级 (PriorityLevel)
Scheduler 任务的优先级与 React 优先级并不一致,因为其不依赖于 React,它的优先级如下。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9// /src/SchedulerPriorities.js export type PriorityLevel = 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5; export const NoPriority = 0; export const ImmediatePriority = 1; export const UserBlockingPriority = 2; export const NormalPriority = 3; export const LowPriority = 4; export const IdlePriority = 5;
除 NoPriority 外,数字越小优先级越高。
任务的开始时间与结束时间
任务调度并不是直接使用任务优先级进行的,而是采用以 当前时间 与 优先级 为基础,计算得到开始时间 startTime 与截止时间 expirationTime,并遵循 最早截止时间 调度。计算逻辑在 unstable_scheduleCallback 中。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50// Max 31 bit integer. The max integer size in V8 for 32-bit systems. // Math.pow(2, 30) - 1 // 0b111111111111111111111111111111 var maxSigned31BitInt = 1073741823; // Times out immediately var IMMEDIATE_PRIORITY_TIMEOUT = -1; // Eventually times out var USER_BLOCKING_PRIORITY_TIMEOUT = 250; var NORMAL_PRIORITY_TIMEOUT = 5000; var LOW_PRIORITY_TIMEOUT = 10000; // Never times out var IDLE_PRIORITY_TIMEOUT = maxSigned31BitInt; // ... function unstable_scheduleCallback(priorityLevel, callback, options) { var currentTime = getCurrentTime(); /* 计算 startTime */ var startTime; if (typeof options === "object" && options !== null) { var delay = options.delay; if (typeof delay === "number" && delay > 0) { startTime = currentTime + delay; } else { startTime = currentTime; } } else { startTime = currentTime; } /* 计算 expirationTime */ var timeout; switch (priorityLevel) { case ImmediatePriority: timeout = IMMEDIATE_PRIORITY_TIMEOUT; break; case UserBlockingPriority: // ... case IdlePriority: // ... case LowPriority: // ... case NormalPriority: default: timeout = NORMAL_PRIORITY_TIMEOUT; break; } var expirationTime = startTime + timeout; // ... }
维护任务的容器:timerQueue, taskQueue
由于任务遵循最早截止时间调度,因此 Scheduler 中用两个基于小顶堆 (min heap) 的优先队列维护它们:
timerQueue:维护了 还未到达开始时间 的任务,根据任务的开始时间 (startTime) 排序;taskQueue:维护了 已经到达开始时间,但执行未结束 的任务,根据任务的过期时间 (expirationTime) 排序,即任务越早过期的越先被执行;
方法 advanceTimers 可以将已经开始了的任务由 timerQueue 转移到 taskQueue 中,Scheduler 在调度时会在多个地方调用这一方法。
其他
callback: 任务中的callback允许返回一个函数,调度时会视为本任务还需要执行的部分;
基于 Host 的基础实现:SchedulerHostConfig
在介绍 Scheduler 核心实现之前,有必要先引入基于宿主环境 (Host,如 浏览器) 的基础实现 SchedulerHostConfig,它们至少需要实现如下方法:(实际上,该文件中不止是实现了与导出了下面的方法)
- 获取当前时间
- 定时执行 callback
- 调度执行 callback(可以有能力将 callback 放到下一次宏队列中执行,分配时间片)
- 是否需要归还控制权给 Host
目前 Scheduler 只支持浏览器环境,默认包来自于 /src/forks/SchedulerHostConfig.default.js。
获取当前时间:getCurrentTime
获取当前时间,实现代码很简单,即获取当前时间。
1 2 3 4 5 6if (typeof performance === "object" && typeof performance.now === "function") { getCurrentTime = () => performance.now(); } else { const initialTime = Date.now(); getCurrentTime = () => Date.now() - initialTime; }
定时执行 callback:requestHostTimeout
直接基于 setTimeout 即可。
1 2 3 4 5requestHostTimeout = function (callback, ms) { taskTimeoutID = setTimeout(() => { callback(getCurrentTime()); }, ms); };
调度执行 callback:requestHostCallback
requestHostCallback 基于 MessageChannel(据说比 setTimeout(callback, 0) 快),保存 callback 后,在下一次宏队列中执行核心方法 performWorkUntilDeadline。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11const channel = new MessageChannel(); const port = channel.port2; channel.port1.onmessage = performWorkUntilDeadline; requestHostCallback = function (callback) { scheduledHostCallback = callback; if (!isMessageLoopRunning) { isMessageLoopRunning = true; port.postMessage(null); } };
performWorkUntilDeadline 是调度的核心方法,该方法会加锁执行,会不断处理 scheduledHostCallback 且每次处理都是一个 Macro Task。处理过程中会维护本次处理的截至时间 deadline(此变量在 shouldYieldToHost 中使用,见下文)。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22const performWorkUntilDeadline = () => { if (scheduledHostCallback !== null) { const currentTime = getCurrentTime(); deadline = currentTime + yieldInterval; // yieldInterval 默认为 5,可能因某些 API 而改变 const hasTimeRemaining = true; try { const hasMoreWork = scheduledHostCallback(hasTimeRemaining, currentTime); if (!hasMoreWork) { isMessageLoopRunning = false; scheduledHostCallback = null; } else { port.postMessage(null); } } catch (error) { port.postMessage(null); throw error; } } else { isMessageLoopRunning = false; } needsPaint = false; };
是否需要归还控制权给 Host:shouldYieldToHost
shouldYieldToHost 用于告知调用方是否应当结束处理 callback 的循环。调用方的结束方法可以是令 scheduledHostCallback 返回的 hasMoreWork 的值为 false。
当 navigator.scheduling.isInputPending 存在时,其实现为:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11shouldYieldToHost = function () { const currentTime = getCurrentTime(); if (currentTime >= deadline) { if (needsPaint || scheduling.isInputPending()) { return true; } return currentTime >= maxYieldInterval; // maxYieldInterval = 300 } else { return false; } };
其中,needsPaint 是 requestPaint 的结果。
不存在时,其实现为
1 2 3shouldYieldToHost = function () { return getCurrentTime() >= deadline; };
核心实现
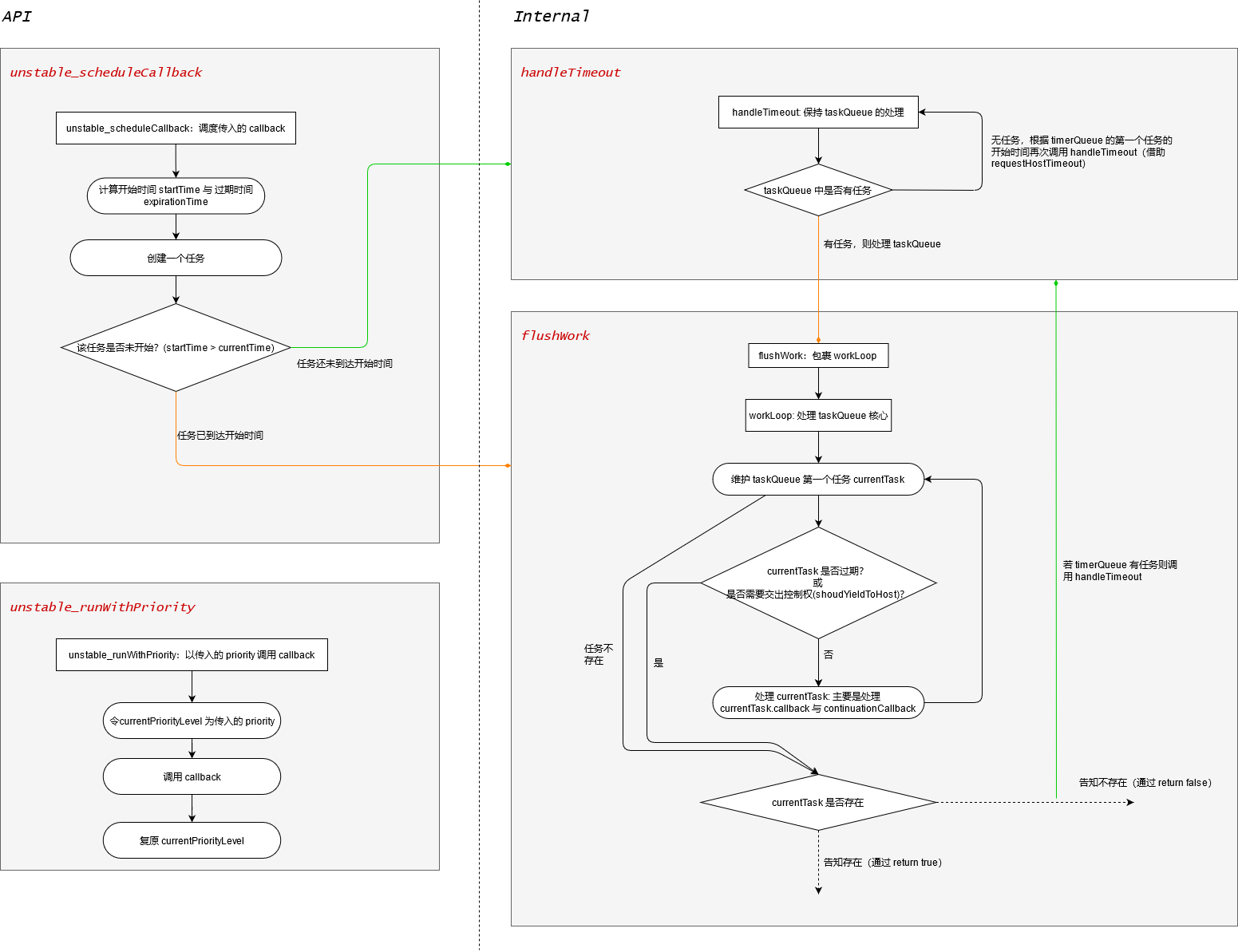
Scheduler 内部的核心实现分为两大块:
handleTimeout:使得在适当的时机调用requestHostCallback(flushWork);flushWork,workLoop:处理taskQueue;
handleTimeout(currentTime)
此方法不会被同时调用,当 timerQueue 中存在任务时会被触发,其用于尝试开启 flushWork 循环。
当 flushWork 循环未开启时,其会检测 taskQueue 是否为空:
- 如非空,则调用
requestHostCallback(flushWork)开始处理taskQueue; - 若为空,则取
timerQueue中的第一个任务 (由于小顶堆的特性,其 startTime 最小),在其应当转入 taskQueue 的时机再次调用handleTimeout(即requestHostTimeout(handleTimeout, firstTimer.startTime - currentTime));
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16function handleTimeout(currentTime) { isHostTimeoutScheduled = false; advanceTimers(currentTime); if (!isHostCallbackScheduled) { if (peek(taskQueue) !== null) { isHostCallbackScheduled = true; requestHostCallback(flushWork); } else { const firstTimer = peek(timerQueue); if (firstTimer !== null) { requestHostTimeout(handleTimeout, firstTimer.startTime - currentTime); } } } }
flushWork(hasTimeRemaining, initialTime) & workLoop(hasTimeRemaining, initialTime)
flushWork 与 workLoop 用于执行 taskQueue 中的任务,这两个方法在执行时都不会被再次调用。
flushWork 不会被直接调用,其调用形式为 requestHostCallback(flushWork)。借助于 requestHostCallback,flushWork 可以将 taskQueue 中的任务分在多个 Macro Task 中执行,而不是只在一个 Macro Task 中就全部执行。workLoop 只会被 flushWork 调用。
flushWork 的主要工作交由 workLoop 完成,其返回值 hasMoreWork 也由 workLoop 决定,自己只是完成一系列其他操作,如:
- cancelHostTimeout。因为 flushWork 已经被执行, handleTimeout 需要转换 task 可能会在此次 flushWork 中被执行,因此先 cancelHostTimeout,待 workLoop 结束后再考虑是否应该 requestHostTimeout;
- 维护 isPerformingWork,保证 flushWork 与 workLoop 在执行时不会被再次调用;
- 保存 currentPriorityLevel,并在结束时复原;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23function flushWork(hasTimeRemaining, initialTime) { // ... · // 取消存在的 handleTimeout 循环 isHostCallbackScheduled = false; if (isHostTimeoutScheduled) { isHostTimeoutScheduled = false; cancelHostTimeout(); } // 加锁 isPerformingWork = true; const previousPriorityLevel = currentPriorityLevel; try { // ... return workLoop(hasTimeRemaining, initialTime); } finally { currentTask = null; currentPriorityLevel = previousPriorityLevel; isPerformingWork = false; // ... } }
workLoop 是处理 taskQueue 的核心方法。在这一方法中,会调用 advanceTimers 更新 taskQueue,后不断从 taskQueue 中取出任务执行,直到当前任务到达过期时间,或需要归还控制权给 Host (shouldYieldToHost())。每次执行 task 结束后,会再次调用 advanceTimers 更新 taskQueue。
处理 taskQueue 的循环结束后,会根据最后一次处理的 task,决定返回值 hasMoreWork 与决定是否需要调用 handleTimeout。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54function workLoop(hasTimeRemaining, initialTime) { let currentTime = initialTime; advanceTimers(currentTime); currentTask = peek(taskQueue); while ( currentTask !== null && !(enableSchedulerDebugging && isSchedulerPaused) ) { if ( currentTask.expirationTime > currentTime && (!hasTimeRemaining || shouldYieldToHost()) ) { // This currentTask hasn't expired, and we've reached the deadline. break; } const callback = currentTask.callback; if (typeof callback === "function") { currentTask.callback = null; currentPriorityLevel = currentTask.priorityLevel; const didUserCallbackTimeout = currentTask.expirationTime <= currentTime; if (enableProfiling) { markTaskRun(currentTask, currentTime); } const continuationCallback = callback(didUserCallbackTimeout); currentTime = getCurrentTime(); // 该 callback 存在继续执行的 callback,则不弹出本任务 if (typeof continuationCallback === "function") { currentTask.callback = continuationCallback; // ... } else { // ... if (currentTask === peek(taskQueue)) { pop(taskQueue); } } advanceTimers(currentTime); } else { pop(taskQueue); } currentTask = peek(taskQueue); } // 根据有无任务返回 true/false // 由于被 flushWork 被 requestHostCallback 包裹,因此返回 true 时会在下一次 // 宏队列中继续执行 workLoop if (currentTask !== null) { return true; } else { const firstTimer = peek(timerQueue); if (firstTimer !== null) { requestHostTimeout(handleTimeout, firstTimer.startTime - currentTime); } return false; } }
API
Scheduler 导出了若干个 API:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20export { ImmediatePriority as unstable_ImmediatePriority, UserBlockingPriority as unstable_UserBlockingPriority, NormalPriority as unstable_NormalPriority, IdlePriority as unstable_IdlePriority, LowPriority as unstable_LowPriority, unstable_runWithPriority, unstable_next, unstable_scheduleCallback, unstable_cancelCallback, unstable_wrapCallback, unstable_getCurrentPriorityLevel, shouldYieldToHost as unstable_shouldYield, unstable_requestPaint, unstable_continueExecution, unstable_pauseExecution, unstable_getFirstCallbackNode, getCurrentTime as unstable_now, forceFrameRate as unstable_forceFrameRate, };
此处只展开介绍两个 API:
unstable_scheduleCallback:以传入的优先级调度 callback;unstable_runWithPriority:以传入的优先级运行 callback;
unstable_scheduleCallback(priorityLevel, callback, options)
此方法用于调度一个 callback。在方法中,会计算任务的开始时间与过期时间,并创建一个 task,根据 task 的 startTime,决定将其加入 timerQueue 还是 taskQueue,并相应的执行 handleTimeout 或 requestHostCallback(flushWork)。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39function unstable_scheduleCallback(priorityLevel, callback, options) { var currentTime = getCurrentTime(); // 计算开始时间 startTime 与过期时间 expirationTime var newTask = { id: taskIdCounter++, callback, priorityLevel, startTime, expirationTime, sortIndex: -1, }; // ... // 根据任务是否已经开始放入相应的队列并调用相应的方法 if (startTime > currentTime) { newTask.sortIndex = startTime; push(timerQueue, newTask); if (peek(taskQueue) === null && newTask === peek(timerQueue)) { if (isHostTimeoutScheduled) { cancelHostTimeout(); } else { isHostTimeoutScheduled = true; } requestHostTimeout(handleTimeout, startTime - currentTime); } } else { newTask.sortIndex = expirationTime; push(taskQueue, newTask); // ... if (!isHostCallbackScheduled && !isPerformingWork) { isHostCallbackScheduled = true; requestHostCallback(flushWork); } } return newTask; }
unstable_runWithPriority(priorityLevel, eventHandler) 【WIP】
此方法会同步执行 eventHandler(),并在执行期间将 currentPriorityLevel 改为 priorityLevel。(其作用 WIP)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21function unstable_runWithPriority(priorityLevel, eventHandler) { switch (priorityLevel) { case ImmediatePriority: case UserBlockingPriority: case NormalPriority: case LowPriority: case IdlePriority: break; default: priorityLevel = NormalPriority; } var previousPriorityLevel = currentPriorityLevel; currentPriorityLevel = priorityLevel; try { return eventHandler(); } finally { currentPriorityLevel = previousPriorityLevel; } }
SchedulerWithReactIntegration:桥接 React 与 Scheduler
SchedulerWithReactIntegration 中大部分 API 是将 React 优先级转为 Scheduler 优先级后直接对接,如 runWithPriority 对接 unstable_runWithPriority。需要注意的非直接对接的 API 有:scheduleSyncCallback, flushSyncCallbackQueue。
scheduleSyncCallback 将 callback 加入 syncQueue,并通过 scheduler_scheduleCallback(Scheduler_ImmediatePriority, flushSyncCallbackQueueImpl) 在下一次 tick(宏任务)中执行并清除 syncQueue(flushSyncCallbackQueueImpl 执行期间会将优先级设置为 ImmediatePriority)。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17export function scheduleSyncCallback(callback: SchedulerCallback) { // Push this callback into an internal queue. We'll flush these either in // the next tick, or earlier if something calls `flushSyncCallbackQueue`. if (syncQueue === null) { syncQueue = [callback]; // Flush the queue in the next tick, at the earliest. immediateQueueCallbackNode = Scheduler_scheduleCallback( Scheduler_ImmediatePriority, flushSyncCallbackQueueImpl ); } else { // Push onto existing queue. Don't need to schedule a callback because // we already scheduled one when we created the queue. syncQueue.push(callback); } return fakeCallbackNode; }
flushSyncCallbackQueue 会同步地执行并清除 syncQueue,期间会将优先级设置为 ImmediatePriority。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47export function flushSyncCallbackQueue(): boolean { // 取消可能存在的 "scheduleSyncCallback" 调度 if (immediateQueueCallbackNode !== null) { const node = immediateQueueCallbackNode; immediateQueueCallbackNode = null; Scheduler_cancelCallback(node); } return flushSyncCallbackQueueImpl(); } function flushSyncCallbackQueueImpl() { if (!isFlushingSyncQueue && syncQueue !== null) { // Prevent re-entrancy. isFlushingSyncQueue = true; let i = 0; // ... try { const isSync = true; const queue = syncQueue; runWithPriority(ImmediatePriority, () => { for (; i < queue.length; i++) { let callback = queue[i]; do { callback = callback(isSync); } while (callback !== null); } }); syncQueue = null; } catch (error) { // If something throws, leave the remaining callbacks on the queue. if (syncQueue !== null) { syncQueue = syncQueue.slice(i + 1); } // Resume flushing in the next tick Scheduler_scheduleCallback( Scheduler_ImmediatePriority, flushSyncCallbackQueue ); throw error; } finally { isFlushingSyncQueue = false; } return true; } else { return false; } }
总结
总结如图,其中橙色线为 requestHostCallback 包裹调用,绿色线为 requestHostTimeout 包裹调用。