React 状态更新原理简析
大体流程
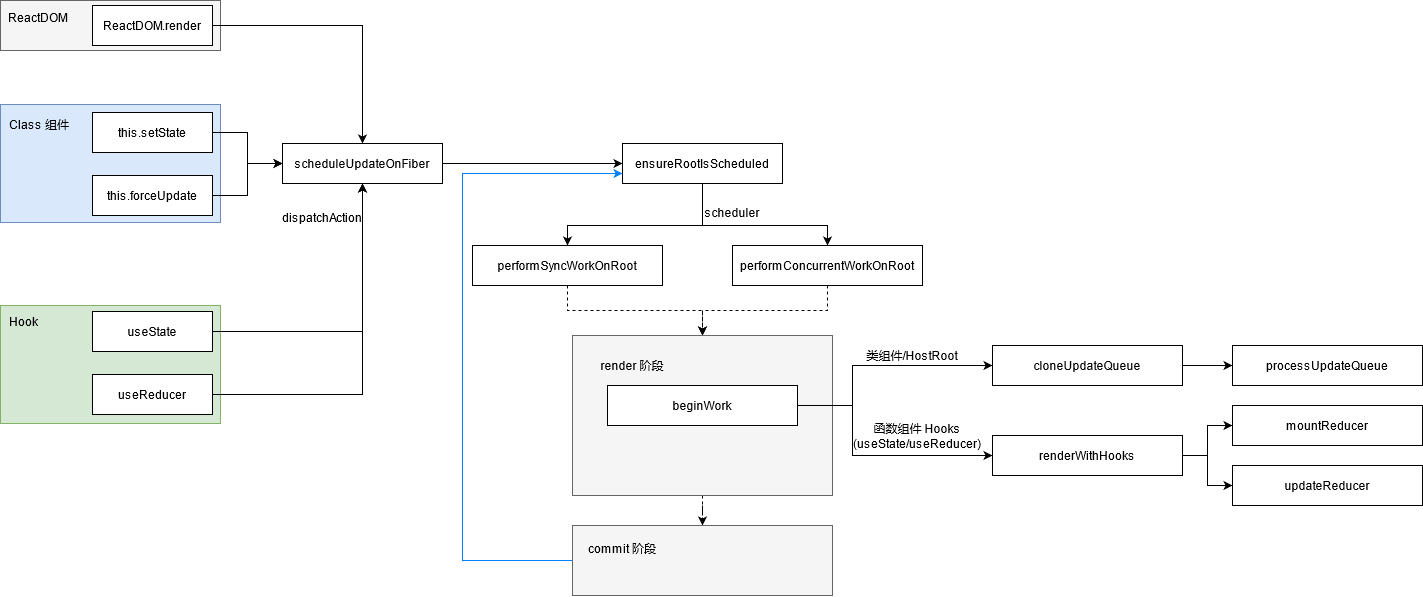
数据结构
Fiber
Fiber 与状态更新有关的属性为:
1 2 3 4 5 6export type Fiber = { flags: Flags; updateQueue: mixed; memoizedState: any; lanes: Lanes; };
Update 与 UpdateQueue (在 HostRoot, ClassComponent 使用)
Update 描述了更新的结构:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13export const UpdateState = 0; export const ReplaceState = 1; export const ForceUpdate = 2; export const CaptureUpdate = 3; export type Update<State> = { eventTime: number; lane: Lane; // 优先级 tag: 0 | 1 | 2 | 3; // 类型,有 UpdateState, ReplaceState, ForceUpdate, CaptureUpdate payload: any; // 更新内容 callback: (() => mixed) | null; // callback next: Update<State> | null; // 指向下一个 Update };
UpdateQueue 存储了 Update:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13export type UpdateQueue<State> = { // 更新前的 state baseState: State; // 触发更新前已有 Update 组成的单链表,firstBaseUpdate 为头,lastBaseUpdate 为尾 firstBaseUpdate: Update<State> | null; lastBaseUpdate: Update<State> | null; shared: { // 触发更新时 Update 组成的循环链表 pending: Update<State> | null; }; // 保存 callback 非空的 Update effects: Array<Update<State>> | null; };
此处触发更新前会有 Update 是因为更新时会跳过低优先级 Update,详见 核心 API 中的 ensureRootIsScheduled。
Update 与 UpdateQueue (Hook)
Hook 中的 Hook, Update, UpdateQueue 与 类组件中的类似。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23export type Hook = { memoizedState: any, baseState: any, // 类似于类组件中的 UpdateQueue.baseState baseQueue: Update<any, any> | null, // 类似于类组件中的 UpdateQueue.firstBaseUpdate 与 UpdateQueue.lastBaseUpdate queue: UpdateQueue<any, any> | null, // updateQueue next: Hook | null, }; type Update<S, A> = { lane: Lane, // 优先级 action: A, // action eagerReducer: ((S, A) => S) | null, // dispatchAction 时保存的 queue.lastRenderedReducer eagerState: S | null, // dispatchAction 时根据 eagerReducer, queue.lastRenderedState, action 提前计算的 state next: Update<S, A>, // next 指针,为环状链表 priority?: ReactPriorityLevel, }; type UpdateQueue<S, A> = { pending: Update<S, A> | null, // update 链表 dispatch: (A => mixed) | null, // useState, useReducer 返回的 dispatch lastRenderedReducer: ((S, A) => S) | null, // 最后一次 mountReducer/updateReducer 的 reducer lastRenderedState: S | null, // 最后一次 mountReducer/updateReducer 的 state };
处理 updateQueue (类组件与 HostRoot)
类组件处理 updateQueue 发生在 render 阶段的 beginWork 中。
cloneUpdateQueue
处理 updateQueue 前,若 current 与 workInProgress 的 updateQueue 引用相同,则会进行浅拷贝。
processUpdateQueue
processUpdateQueue 负责处理 updateQueue,其中核心流程为:
- 将
shared.pending转为单链表并同时接到 current 与 workInProgress 的baseQueue后,并清空原shared.pending引用; - 遍历
baseQueue,维护新的 updateQueue:
baseState:直到第一个不满足优先级的 update 为止,通过处理满足优先级的 update 调用getStateFromUpdate计算得到的新的 state;effects:处理满足优先级的 update 后,根据update.callback维护;firstBaseUpdate,lastBaseUpdate:由 第一个不满足优先级的 Update 与其后的 Update 组成;
- 当
baseQueue遍历完成后,会检测shared.pending是否为空,若非空则会重复步骤 1, 2; - 维护 workInProgress fiber 相关属性
lanes:将不满足优先级的 update 通过mergeLanes得到的 lane;memoizedState:通过处理所有满足优先级的 update 计算得到的新的 state;
需要注意:
- 步骤 1 中 “同时接到 current 与 workInProgress 的
baseQueue后” 是为了防止中断后造成 update 丢失; workInProgress.memoizedState与updateQueue.baseState相比,没有 “遇到第一个不满足优先级的 update” 的限制。因为baseState是计算新 state 的基础,新 state 通过firstBaseUpdate与lastBaseUpdate组成的链表构成。而memoizedState是 fiber 计算得到的 state;baseQueue遍历过程中,shared.pending可能会由于 update 内部触发更新而导致非空,这是需要进行步骤 3 的原因;
处理 updateQueue (函数组件 Hook)
函数组件的 useState/useReducer 处理 updateQueue 发生在 render 阶段的 beginWork 中,由 renderWithHooks 调用 mountReducer/updateReducer。
mountReducer
初始化:
hook.memoizedState,hook.baseStatehook.queuedispatch
返回 [hook.memoizedState, dispatch]
updateReducer
与类组件的 processUpdateQueue 类似:
- 合并 workInProgress 的 hook 的
baseQueue与queue.pending组成新的环状链表,并设置在 current 的 hook 的baseQueue上; - 遍历合并后的 updateQueue,同样考虑 lane 并维护
hook.baseState,hook.baseQueue,queue.lastRenderedState
与类组件的 processUpdateQueue 不同的是:
- 若满足
update.eagerReducer === reducer,会直接采用在dispatchAction中计算得到的eagerState(因此连续执行setState(prev => ...)时prev是一致的),否则会基于计算时的newState与传入的reducer计算reducer(newState, update.action)
核心 API
scheduleUpdateOnFiber
为当前 fiber 调度一次更新。具体流程为:
markUpdateLaneFromFiberToRoot:从当前 fiber 到根更新 lane,并返回 fiber root;- 调用
ensureRootIsScheduled以确保 fiber root 被调度 (实际上会有优化,如当为SyncLane且不在 render 或 commit 阶段时直接执行performSyncWorkOnRoot);
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54export function scheduleUpdateOnFiber( fiber: Fiber, lane: Lane, eventTime: number ) { checkForNestedUpdates(); warnAboutRenderPhaseUpdatesInDEV(fiber); const root = markUpdateLaneFromFiberToRoot(fiber, lane); if (root === null) { // ... return null; } // 标记 root 有 pending update markRootUpdated(root, lane, eventTime); // ... const priorityLevel = getCurrentPriorityLevel(); if (lane === SyncLane) { if ( (executionContext & LegacyUnbatchedContext) !== NoContext && (executionContext & (RenderContext | CommitContext)) === NoContext ) { schedulePendingInteractions(root, lane); // unbatched 且不在渲染时则不通过 scheduler 直接调度 performSyncWorkOnRoot(root); } else { ensureRootIsScheduled(root, eventTime); schedulePendingInteractions(root, lane); if (executionContext === NoContext) { resetRenderTimer(); flushSyncCallbackQueue(); } } } else { if ( (executionContext & DiscreteEventContext) !== NoContext && // Only updates at user-blocking priority or greater are considered // discrete, even inside a discrete event. (priorityLevel === UserBlockingSchedulerPriority || priorityLevel === ImmediateSchedulerPriority) ) { // 维护 rootsWithPendingDiscreteUpdates // ... } ensureRootIsScheduled(root, eventTime); schedulePendingInteractions(root, lane); } // ... }
ensureRootIsScheduled
此 API 确保 fiber root 被调度:
- 获取优先级(lanePriority);
- 若已存在不同优先级的调度任务,说明有任务正在进行,将其取消(此处存在不同优先级的调度任务意味着此次优先级更高);
- 通过 scheduler 调度
performSyncWorkOnRoot/performConcurrentWorkOnRoot;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50function ensureRootIsScheduled(root: FiberRoot, currentTime: number) { const existingCallbackNode = root.callbackNode; // 防饥饿 markStarvedLanesAsExpired(root, currentTime); // 下一次渲染使用的 lanes const nextLanes = getNextLanes( root, root === workInProgressRoot ? workInProgressRootRenderLanes : NoLanes ); // 即 return_highestLanePriority const newCallbackPriority = returnNextLanesPriority(); // ... // 当前存在调度任务 if (existingCallbackNode !== null) { const existingCallbackPriority = root.callbackPriority; // 优先级不变时,复用调度,直接退出 if (existingCallbackPriority === newCallbackPriority) { return; } // 优先级改变时,取消现有调度 cancelCallback(existingCallbackNode); } // 调度新任务 let newCallbackNode; if (newCallbackPriority === SyncLanePriority) { newCallbackNode = scheduleSyncCallback( performSyncWorkOnRoot.bind(null, root) ); } else if (newCallbackPriority === SyncBatchedLanePriority) { newCallbackNode = scheduleCallback( ImmediateSchedulerPriority, performSyncWorkOnRoot.bind(null, root) ); } else { const schedulerPriorityLevel = lanePriorityToSchedulerPriority(newCallbackPriority); newCallbackNode = scheduleCallback( schedulerPriorityLevel, performConcurrentWorkOnRoot.bind(null, root) ); } root.callbackPriority = newCallbackPriority; root.callbackNode = newCallbackNode; }
在 commit 阶段的最后,会再次调用此 API 已确保所有的任务都被调度(如之前取消过任务,可能会在此次调用中被重新处理)。
状态更新相关 API
ReactDOM.renderthis.setStatethis.forceUpdateuseStateuseReducer
上述 API 都会创建 Update 对象并调用 scheduleUpdateOnFiber。
另外,可以了解到:
- 类组件的 API
this.setState,this.forceUpdate实际上是调用 updaterclassComponentUpdater,其在 render 阶段的 beginWork 中注入; - Hook
useState实际上即 reducer 为basicStateReducer的useReducer,它们返回的数组中的第二项实际上为dispatchAction; - 上述 API 通过
requestUpdateLane得到创建 update 以及调用scheduleUpdateOnFiber时使用的 lane;
dispatchAction (Hook)
useState/useReducer 返回的数组的第二项为 dispatch,会间接调用 dispatchAction。dispatchAction 中会生成 update 对象并维护 queue.pending。需要注意,update 对象中的 eagerReducer 与 eagerState 的维护是基于 queue.lastRenderedReducer 与 queue.lastRenderedState 计算的,因此在一次 update 中调用 dispatch 时的 state 都是相同的。
优先级(WIP)
requestUpdateLane (WIP)
目前对于 legacy 模式,均返回 SyncLane。目前 React 18 正在稳定的路上,待后续学习新的 API 与模式后再补充 QAQ
其他
this.setState 的同步与异步问题(legacy 模式)
this.setState 会调用 requestUpdateLane -> scheduleUpdateOnFiber,首先明确:
- legacy 模式下
requestUpdateLane均获得SyncLane
以下分情况讨论:
- 原生事件、setTimeout 等:
scheduleUpdateOnFiber中 executionContext 为NoContext下,因此调用ensureRootIsScheduled并调用flushSyncCallbackQueue,后调用performSyncWorkOnRoot,因而 render 阶段被同步执行,processUpdateQueue此时处理完成新的 state,因此表现为 同步; - 生命周期方法:与原生事件相比,区别在于
executionContext不为 null,因此不会在本次宏任务中执行performSyncWorkOnRoot,表现为 异步; - React 事件方法:
executionContext至少会被打上EventContext,因此同理表现为 异步;