Tapable 原理简析
前言
tapable 是 webpack 支持插件所设计的库,同时 webpack 本身也构建在其之上。tapable 本质上使用 发布订阅模式 实现,此模式在前端中应用甚广,熟悉此模式的读者应该已经知道如何实现一个简单的 tapable。因此,本文不打算造轮子,而是分析 tapable 源码,同时尝试分析其中的值得学习的地方,并尝试分析 tapable 自身的优劣势。
简单应用的例子
Hook 的种类
tapable 提供的 Hook 如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11const { SyncHook, SyncBailHook, SyncWaterfallHook, SyncLoopHook, AsyncParallelHook, AsyncParallelBailHook, AsyncSeriesHook, AsyncSeriesBailHook, AsyncSeriesWaterfallHook, } = require("tapable");
可以将他们按两种维度分类:
Basic, Waterfall, Bail, Loop
- Basic:最基础的 hook,call 即触发。
- Waterfall:具有 pipe 形式的 hook,即触发时上一个 function 的返回值会传递给下一个 function。
- Bail:具有 any 形式的 hook,即触发时任意一个 function 返回值时,该 hook 会直接退出,不会等待其他 function 完成。
- Loop:任意一个 function 有返回值时,将会重新从第一个 function 开始,直到所有 function 返回
undefined。
Sync, AsyncSeries, AsyncParallel
- Sync:同步,支持
tap。 - AsyncSeries:异步串行,支持
tap,tapAsync,tapPromise。 - AsyncParallel:异步并行,支持
tap,tapAsync,tapPromise。
源码的简单分析
结构
目前 tapable 的文件可以分为四类:
- Hook:Hook 抽象类
- HookCodeFactory: Hook call 系列方法工厂抽象类
- Hook 与 HookCodeFactory 类:
- SyncHook
- SyncBailHook
- ...
- helper:
- HookMap
- MultiHook
笔者对其分析只涉及前三者(即不分析 helper),同时会省略大量的细节处理,详细实现细节见 官方 repo。
tap 系列方法
tap 系列方法为 tap, tapAsync, tapPromise,下称 tap*。tap* 充当了发布订阅模式中的 订阅,实现时内部容器(如数组)插入 listener 即可(由于源码中将 listener 称为 tap,因此下称 tap)。
call 系列方法
call 系列方法为 call, callAsync, promise,下称 call*。在通常的实现下,可以通过在 call* 中遍历 taps 并调用来实现。在 tapable 的实现中,其通过生成代码后 new Function 创建函数实现。(原因见 此 issue,笔者认为这相当惊艳!)下图表述了 call* 逻辑实现。
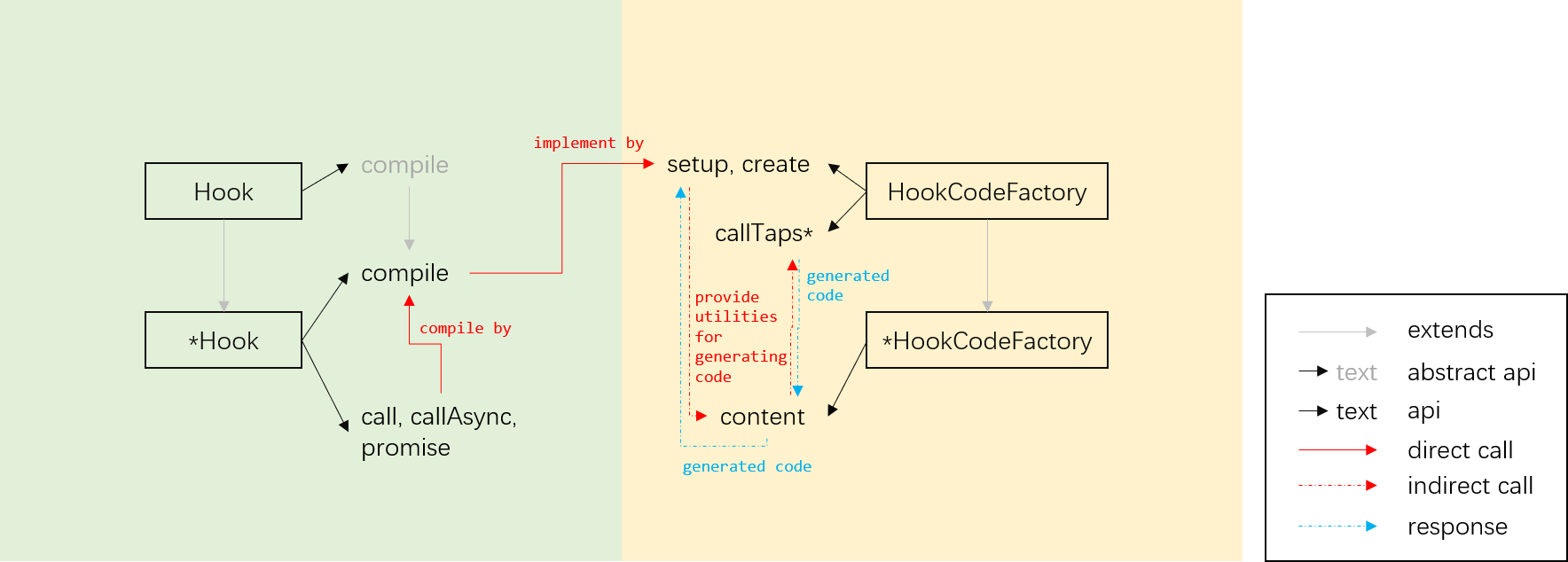
图中,*Hook 表示 Hook 类(SyncHook, SyncBailHook 等),*HookCodeFactory 表示 HookCodeFactory 类。
基于目前的实现,可以思考几个问题:
- 如何生成代码?
- 如何解耦与复用?如果未来新增了 Hook,可以怎样尽可能避免修改抽象类。
- 如何实现缓存?因为基于代码生成,可以将生成的函数缓存下来,提高性能。
代码生成、解耦与复用
总的来说,代码生成分为几个部分:
HookCodeFactory抽象类中的create生成全部代码,其中为*HookCodeFactory中的content提供控制整个流程关键处运行的 helper api;*HookCodeFactory中的content利用控制整个流程运行的 helper api,间接控制taps[i]与整个流程关键处运行;HookCodeFactory抽象类中的callTap直接控制taps[i]关键处运行,callTapsSeries,callTapsParallel等(下称callTaps*)直接控制整个关键处运行;
上述中的 “关键处” 为笔者定义,在源代码中指:
- onError
- onResult: 得到结果时,会有结果返回
- onDone:完成时,与
onResult相比,没有返回值
下面看部分 API 是如何实现的。
HookCodeFactory.create
根据 call* 类型生成代码。
如当 call(源码中对应 sync) 时:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12fn = new Function( this.args(), '"use strict";\n' + this.header() + this.contentWithInterceptors({ onError: (err) => `throw ${err};\n`, onResult: (result) => `return ${result};\n`, resultReturns: true, onDone: () => "", rethrowIfPossible: true, }) );
当 promise (源码中对应 promise)时:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28let errorHelperUsed = false; const content = this.contentWithInterceptors({ onError: (err) => { errorHelperUsed = true; return `_error(${err});\n`; }, onResult: (result) => `_resolve(${result});\n`, onDone: () => "_resolve();\n", }); let code = ""; code += '"use strict";\n'; code += this.header(); code += "return new Promise((function(_resolve, _reject) {\n"; if (errorHelperUsed) { code += "var _sync = true;\n"; code += "function _error(_err) {\n"; code += "if(_sync)\n"; code += "_resolve(Promise.resolve().then((function() { throw _err; })));\n"; code += "else\n"; code += "_reject(_err);\n"; code += "};\n"; } code += content; if (errorHelperUsed) { code += "_sync = false;\n"; } code += "}));\n"; fn = new Function(this.args(), code);
其中,
header():创建必要的变量,如context,taps等;args():获取参数字符串,允许通过before,after参数向前后插值,内部数组为_args;
HookCodeFactory.contentWithInterceptors
HookCodeFactory.contentWithInterceptors 会在考虑拦截器的情况下调用 *HookCodeFactory.content
因此 content 拿到的是参数是一系列 helper api。
HookCodeFactory.callTaps*
callTaps* 由 content 调用,下面只看 callTapsSeries 的实现,其余实现有兴趣读者可自行查看源码。
callTapsSeries 由串行 hook 调用,完整代码为(笔者在源代码的基础上补充注释):
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56// 参数由 *HookCodeFactory.content 生成,个别 helper 形式如: // onResult(i, result, done, doneBreak) // onError(i, error, done, doneBreak) // ... // 他们控制 taps[i] 在关键处的运行,此处往下看 callTap 的实现便可知 callTapsSeries({ onError, onResult, resultReturns, onDone, doneReturns, rethrowIfPossible }) { if (this.options.taps.length === 0) return onDone(); const firstAsync = this.options.taps.findIndex(t => t.type !== "sync"); const somethingReturns = resultReturns || doneReturns; let code = ""; // 生成代码的函数 let current = onDone; let unrollCounter = 0; // 从后往前遍历,这样由于 current 维护的是前一次(或前几次,取决于 unroll)应当生成的内容 // 因此在执行末尾处调用 current 即可,无需递归(这里的末尾不是位置末尾,而是逻辑执行顺序末尾) for (let j = this.options.taps.length - 1; j >= 0; j--) { const i = j; const unroll = current !== onDone && (this.options.taps[i].type !== "sync" || unrollCounter++ > 20); if (unroll) { unrollCounter = 0; code += `function _next${i}() {\n`; code += current(); code += `}\n`; current = () => `${somethingReturns ? "return " : ""}_next${i}();\n`; } const done = current; const doneBreak = skipDone => { if (skipDone) return ""; return onDone(); }; // 从 content api 来的 helper api 间接控制 taps[i] 在关键处的逻辑 const content = this.callTap(i, { onError: error => onError(i, error, done, doneBreak), onResult: onResult && (result => { return onResult(i, result, done, doneBreak); }), onDone: !onResult && done, rethrowIfPossible: rethrowIfPossible && (firstAsync < 0 || i < firstAsync) }); current = () => content; } code += current(); return code; }
HookCodeFactory.callTap
callTap 为执行 taps[i] 的逻辑,会区分 call* 执行。(毕竟 create 中为每个 call* 创建的函数形式不一样)
此处仅看 promise 的实现代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31callTap(tapIndex, { onError, onResult, onDone, rethrowIfPossible }) { let code = ""; // ... interceptors 部分 code += `var _fn${tapIndex} = ${this.getTapFn(tapIndex)};\n`; const tap = this.options.taps[tapIndex]; switch (tap.type) { // ... sync 部分 // ... async 部分 case "promise": code += `var _hasResult${tapIndex} = false;\n`; code += `var _promise${tapIndex} = _fn${tapIndex}(${this.args({ before: tap.context ? "_context" : undefined })});\n`; code += `if (!_promise${tapIndex} || !_promise${tapIndex}.then)\n`; code += ` throw new Error('Tap function (tapPromise) did not return promise (returned ' + _promise${tapIndex} + ')');\n`; code += `_promise${tapIndex}.then((function(_result${tapIndex}) {\n`; code += `_hasResult${tapIndex} = true;\n`; if (onResult) { code += onResult(`_result${tapIndex}`); } if (onDone) { code += onDone(); } code += `}), function(_err${tapIndex}) {\n`; code += `if(_hasResult${tapIndex}) throw _err${tapIndex};\n`; code += onError(`_err${tapIndex}`); code += "});\n"; break; } return code; }
*HookCodeFactory.content
最后看看 *HookCodeFactory.content 如何实现。
AsyncSeriesWaterfallHook:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14content({ onError, onResult, onDone }) { return this.callTapsSeries({ onError: (i, err, next, doneBreak) => onError(err) + doneBreak(true), onResult: (i, result, next) => { let code = ""; code += `if(${result} !== undefined) {\n`; code += `${this._args[0]} = ${result};\n`; code += `}\n`; code += next(); return code; }, onDone: () => onResult(this._args[0]) }); }
回到最开始的问题:如何复用逻辑与解耦?
通过 “关键处” 运行逻辑控制,这个过程对于 *HookCodeFactory 只需要修改 content 即可,并且不需要考虑 call* 的类型。
缓存
官方目前通过 delegate 实现缓存,此处直接贴 call 的代码。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13const CALL_DELEGATE = function (...args) { // _createCall 会生成代码并生成函数 this.call = this._createCall("sync"); return this.call(...args); }; class Hook { constructor(args = [], name = undefined) { // ... this._call = CALL_DELEGATE; this.call = CALL_DELEGATE; // ... } }
拦截器 (interceptors) 【WIP】
WIP