2023-08-04
Tokio Slab 库
前言
最近在 crates.io 搜索 memory allocator 的时候,无意中看到了 tokio 的 slab 库。感兴趣于是看了其中的实现并实现了一版 C++ 实现的 Slab。
Tokio Slab 库的作用与运行机制
slab 库用于对某一类型 T 做内存分配器,其中的内存是预先分配的,比通用的内存分配具备更高的性能。以下是文档中给出的示例:
Rust
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10let mut slab = Slab::new(); let hello = slab.insert("hello"); let world = slab.insert("world"); assert_eq!(slab[hello], "hello"); assert_eq!(slab[world], "world"); slab[world] = "earth"; assert_eq!(slab[world], "earth");
该库的实现本质上是数组 + 链表。
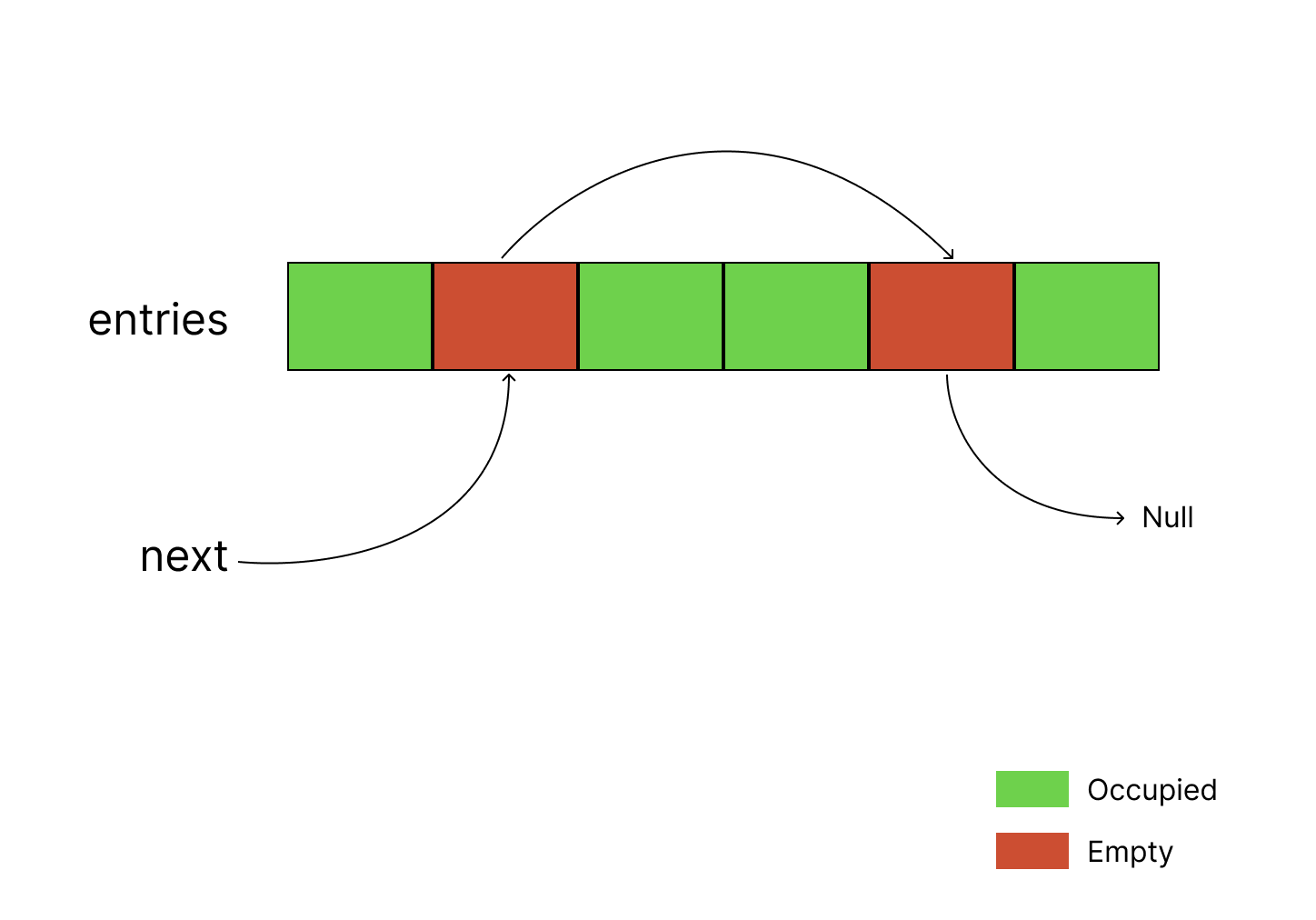
内部维护了:
- entries: 预分配的数组,包含两种状态
- Occupied: 该位置存在数据,存在
T类型对象 - Empty: 该位置不存在数据,记录了下一个 Empty 所在的位置
- Occupied: 该位置存在数据,存在
- next: 第一个 Empty 所在的位置
Rust
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19#[derive(Clone)] enum Entry<T> { // Empty Vacant(usize), Occupied(T), } #[derive(Clone)] pub struct Slab<T> { // Chunk of memory entries: Vec<Entry<T>>, // Number of Filled elements currently in the slab len: usize, // Offset of the next available slot in the slab. Set to the slab's // capacity when the slab is full. next: usize, }
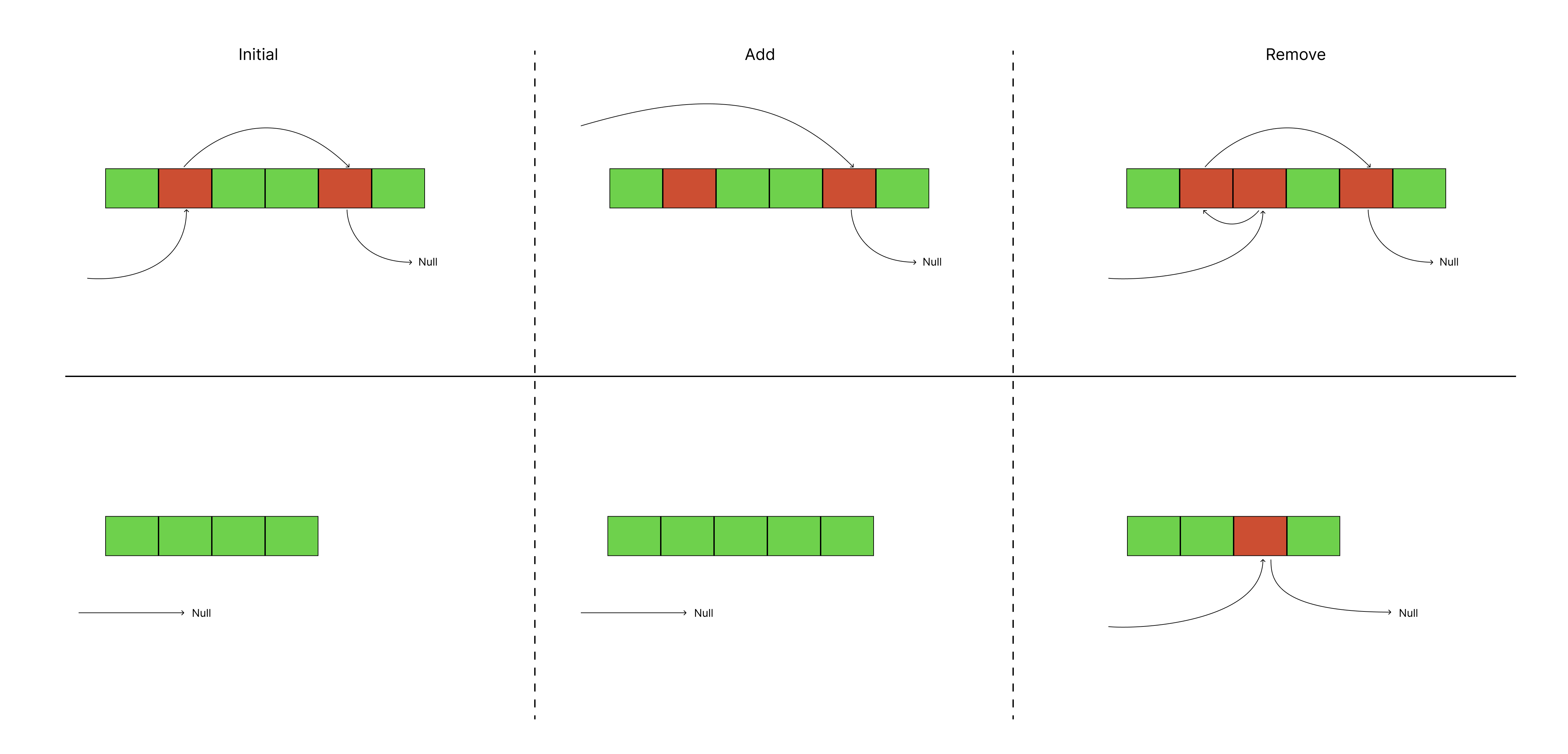
因此 Occupied 本身是数组,而 Empty 组成了链表。当发生了元素插入与删除时,需要同时维护数组与链表的性质。
Tokio Slab 的优缺点
优点:高性能
Tokio Slab 用于为单类型对象频繁分配内存的情况,由于预分配的连续的内存,可以避免频繁分配释放的内存,具有较高的性能。
为什么频繁分配释放内存慢?频繁分配释放内存会造成 内存碎片,这样当需要分配新的内存时,由于寻找空闲的并且空间大于所需空间的内存块,这个过程中遍历到的空间小于所需内存的内存块会变多,整体速度会下降。
缺点:内存占用
当发生元素删除操作时,只是 entries 数组中将其标记为 Empty,而无法真的将这块空间释放掉。因此,相对于通用的分配释放内存操作,Slab 分配器会占用更多的内存。
在 Tokio Slab 中,有个 compact 的方法,能够减少内存占用,其内部实现是:
- 去掉末尾 Empty 的元素,并重新构造 next 链表
- 当传入外部
rekey(value, from, to) -> bool方法时,外部需要处理 key 变更的行为,这样可以将空闲的 Empty 区域填上,能去掉更多的 Empty 元素
缺点:内存复制
由于 entries 是个 Vec,当发生元素的插入或者 compact 行为时,会发生内存重分配与拷贝。
一种分页的 Slab 内存分配器的 C++ 实现
基于 Tokio Slab,笔者实现了一种分页的 Slab 分配器,其结构为:
C++
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30template <typename T> class PagedArray { static constexpr uint16_t BITS = 11; // 预分配数组容量,这里是 1024 static constexpr uint16_t MAX_SIZE = 1 << BITS; struct Inner { std::unique_ptr<T[]> array = nullptr; // 当前数组大小 uint16_t size = 0; // 非 Empty 的数量 uint16_t notErasedSize = 0; }; uint32_t size_ = 0; std::vector<Inner> list_; }; template <typename T> struct Slab { union Data { T value; uint32_t next = UINT_MAX; }; struct WT { bool hasValue = false; Data data; }; PagedArray<WT> allocs; uint32_t next = UINT_MAX; // ... };
这里的存储结构与 Tokio Slab 的定义基本一致,除了将 Vec 换成 PagedArray,替换的优缺点如下:
优点:
- 不需要一大段连续内存,且不会发生内存重分配与复制行为
- 当进行
compact时,如果每一页全都是 Empty 元素,那么一整页的内存都可以被释放掉,更容易释放内存空间
缺点:
- 需要多次分配每一页的内存,性能上会差一些
笔者这里不阐述完整的实现,完整的代码放在了 Github Gist 上。